People with thalassemia minor or trait usually do not need blood transfusions because they either do not have anemia or have only a mild anemia. Epidemiology Approximately 5 percent of the worlds population has a globin variant but only 17 percent has alpha or beta thalasse-mia.
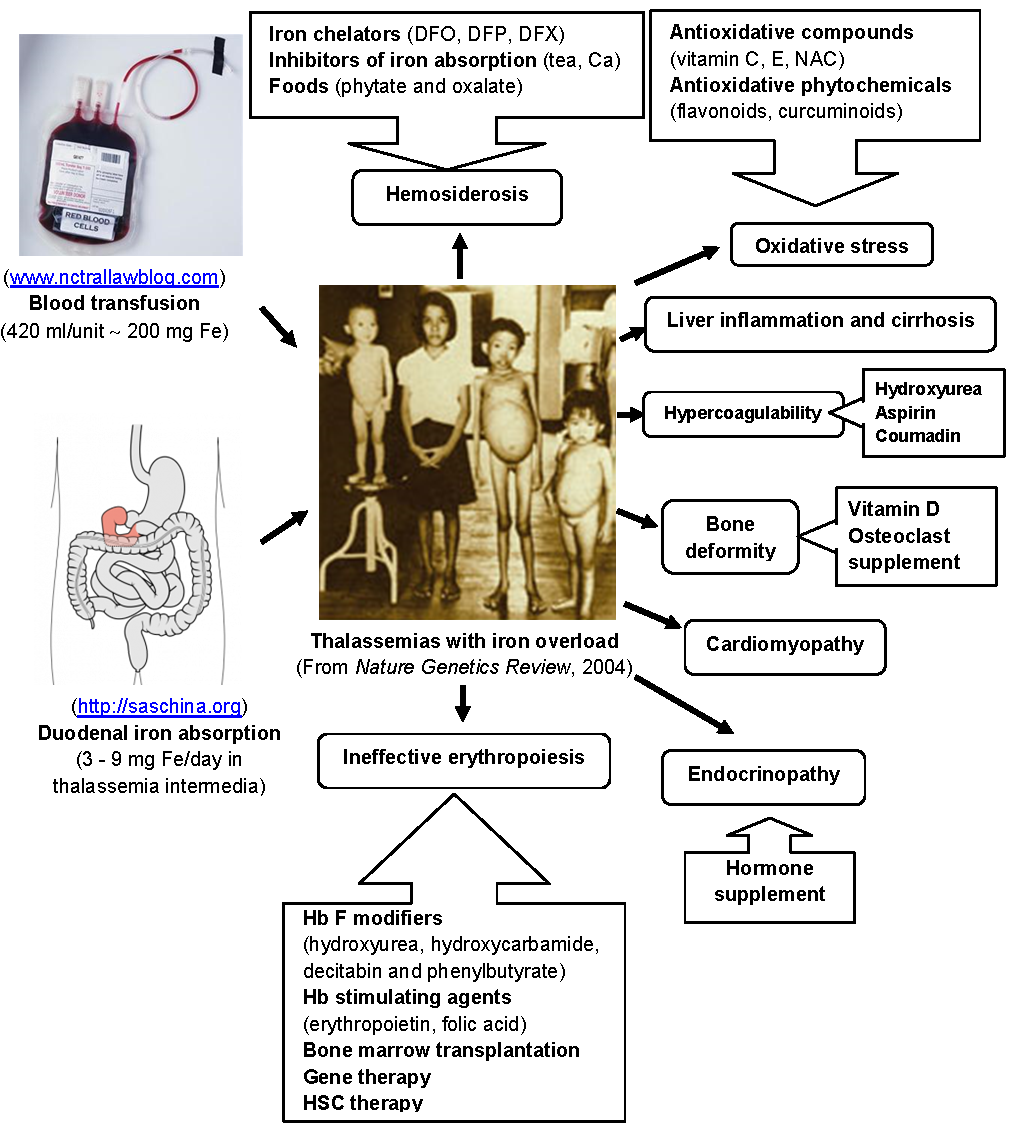 Antioxidants As Complementary Medication In Thalassemia Intechopen
Antioxidants As Complementary Medication In Thalassemia Intechopen
Management of the broad spectrum of phenotypes requires the careful use of red blood transfusions supportive care monitoring and management of iron overload.
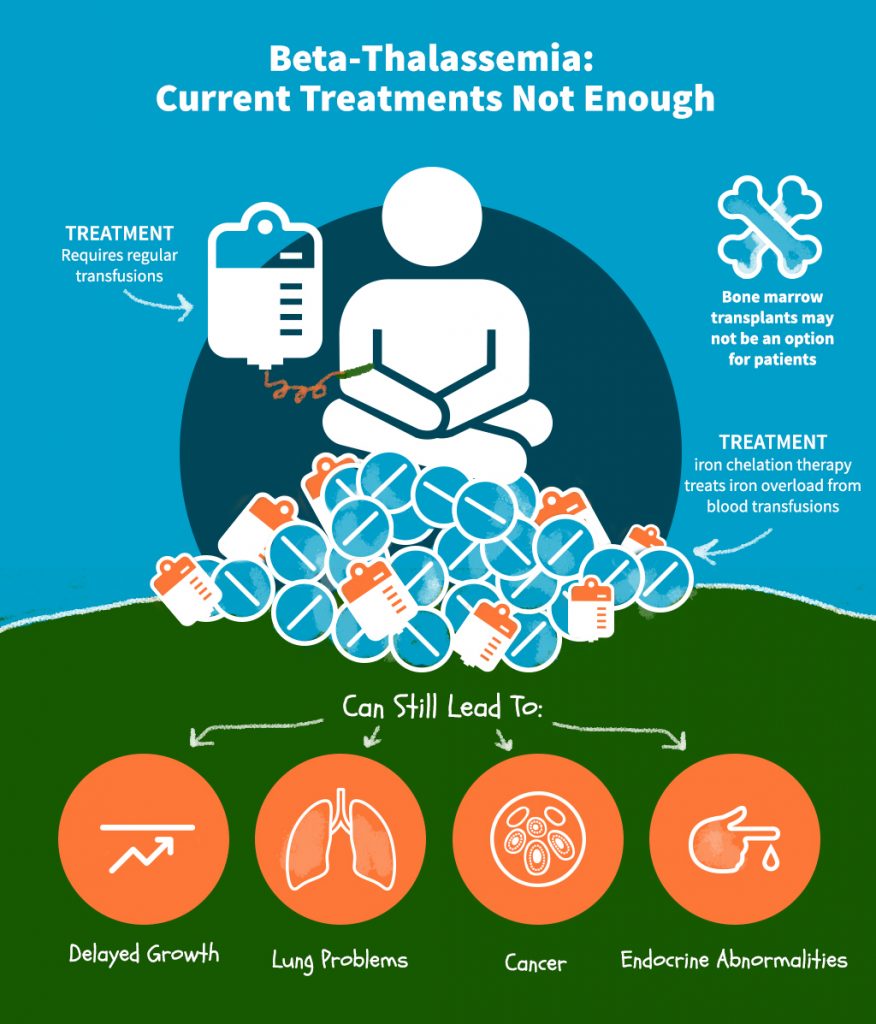
Beta thalassemia treatment. Treatment for thalassemia has dramatically improved. Beta thalassemia intermedia is a clinical diagnosis of a patient characterized by a less severe chronic anemia and a more variable clinical phenotype. Folic acid can help red blood cells develop.
Beta thalassemia is a hereditary disease allowing for a preventative treatment by carrier screening and prenatal diagnosis. Routine blood transfusions are necessary to maintain hemoglobin levels at 9-10gdL. For severe beta thalassemia you or your child may need to get blood transfusions a treatment called chelation therapy that removes excess iron from your body or surgery.
Children and adults with thalassaemia will be supported by a team of different healthcare professionals working together at a specialist thalassaemia centre. β-Thalassemia Major Ongoing treatment is required in individuals suffering from β-thalassemia major. Several studies have reported an increased incidence 1630 of arthropathy in beta-thalassaemia patients on deferiprone therapy 26 5053.
Work with your healthcare provider to stay healthy and reduce complications of the disease. However this treatment can also lead to further complications due to an excess of iron. In this article the authors discuss recommendations for.
Unfortunately many patients die prematurely or develop morbid preventable complications. Beta-thalassemia is a group of frequent genetic disorders resulting in the synthesis of little or no β-globin chains. Treatment of beta-thalassemia The striking improvement in the life expectancy of patients with homozygous beta-thalassemia observed over the past three decades is mainly due to the institution of adequate transfusion regimens and effective iron chelation therapy with nightly subcutaneous desferrioxamine.
The treatment options for severe forms of thalassemia. The prognosis appears pa. Treatment of beta thalassemia may include medicines and regular blood transfusions.
It can be prevented if one parent has normal genes giving rise to screenings that empower carriers to select partners with normal hemoglobin. Beta thalassemia major is a clinical diagnosis referring to a patient who has a severe form of the disease and requires chronic transfusions early in life. In our description of treatment strategies we focus on how we deal with clinical manifestations and long-term complications using the most effective current treatment methods for β-thalassemia.
Life-long red blood cell transfusion iron chelation splenectomy. Patients should live full lives with careers and children of their own. Many times people with thalassemia are prescribed a supplemental B vitamin known as folic acid to help treat anemia.
Globin chain imbalance leads to a complex physiologic cascade of hemolytic anemia ineffective erythropoiesis and iron overload. Beta thalassemias are a significant global health problem. Treatment with folic acid is usually done in addition to other therapies.
Many thalassaemic patients are transfusion dependent and thus are managed with chelation therapy. Thalassaemia usually requires lifelong treatment with blood transfusions and medication. Outcomes are far better for patients whose care is coordinated by thalassemia centers Modell B Khan M and Darlison M.
Novel approaches are being developed to correct the resulting αβ-globin chain imbalance in an effort to move beyond the palliative management of this disease and the complications of its treatment eg. The discussion of disease management focuses on our use of transfusion therapy and the newly developed oral iron chelators deferiprone and deferasirox. This treatment is also known as a.
Survival in beta thalassaemia major in. Stem cell transplants are a treatment option that can potentially cure beta βthalassemia Beta βThalassemia a genetic blood disorder that reduces or eliminates the production of βglobin by addressing the disease at the genetic level.
 Gene Therapy For Beta Thalassemia Updated Perspectives Tacg
Gene Therapy For Beta Thalassemia Updated Perspectives Tacg
 Gene Therapy Shows Durable Efficacy For Transfusion Dependent Beta Thalassemia
Gene Therapy Shows Durable Efficacy For Transfusion Dependent Beta Thalassemia
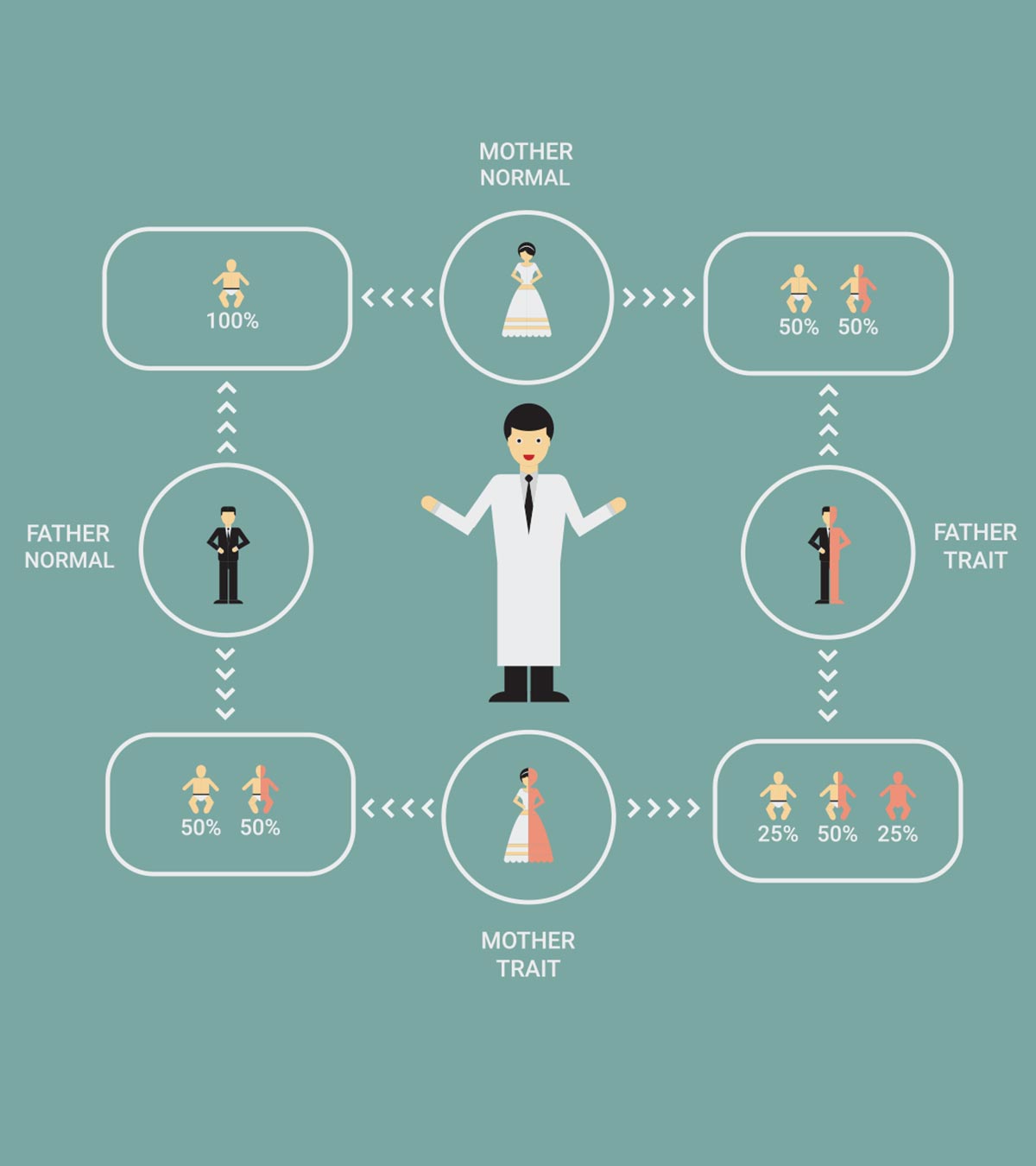 Beta Thalassemia In Children Causes Symptoms Treatment
Beta Thalassemia In Children Causes Symptoms Treatment
 New Therapeutic Trends For Beta Thalassemia
New Therapeutic Trends For Beta Thalassemia
 A Paradigm Shift On Beta Thalassaemia Treatment How Will We Manage This Old Disease With New Therapies Sciencedirect
A Paradigm Shift On Beta Thalassaemia Treatment How Will We Manage This Old Disease With New Therapies Sciencedirect
 Expenses For Treating Complications Of B Thalassemia Major Download Table
Expenses For Treating Complications Of B Thalassemia Major Download Table
 Orchard S Gene Therapy Shows Potential In Treating Patients With Beta Thalassemia
Orchard S Gene Therapy Shows Potential In Treating Patients With Beta Thalassemia
 Thalassemia Causes Treatment Options And Long Term Health Outcomes Nova Science Publishers
Thalassemia Causes Treatment Options And Long Term Health Outcomes Nova Science Publishers
Treatment Of Beta Thalassemia With Chinese Herbs
 Current And Future Therapies For Beta Thalassemia Major Hemoglobin Download Scientific Diagram
Current And Future Therapies For Beta Thalassemia Major Hemoglobin Download Scientific Diagram
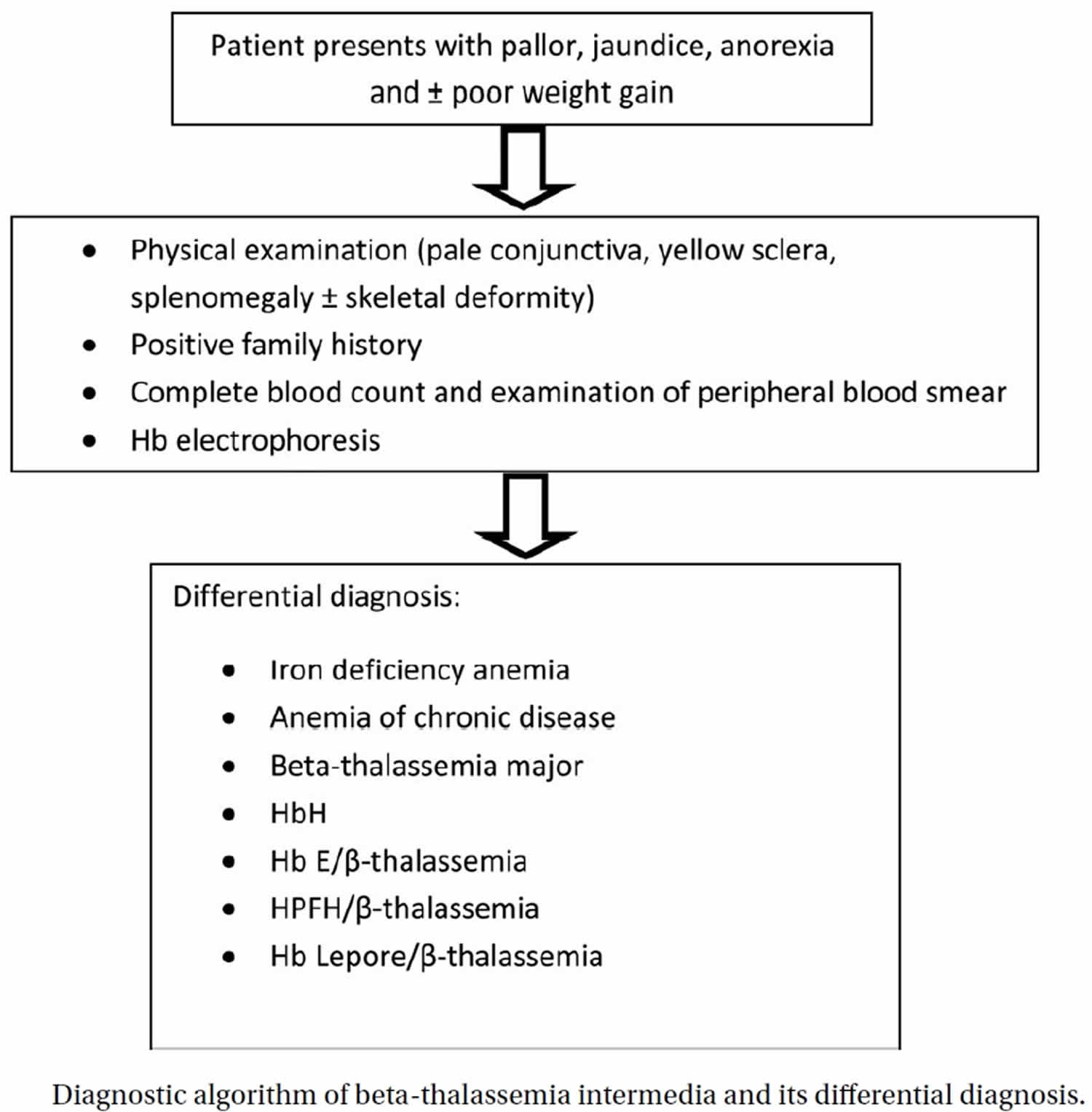 Thalassemia Intermedia Beta Thalassemia Intermedia Causes Symptoms Treatment Prognosis
Thalassemia Intermedia Beta Thalassemia Intermedia Causes Symptoms Treatment Prognosis
Intrauterine Therapy For Alpha Thalassemia Major A Multidisciplinary Center Thalassemia Com
Beta Thalassemia Major Signs Symptoms And Treatment Calgary Guide
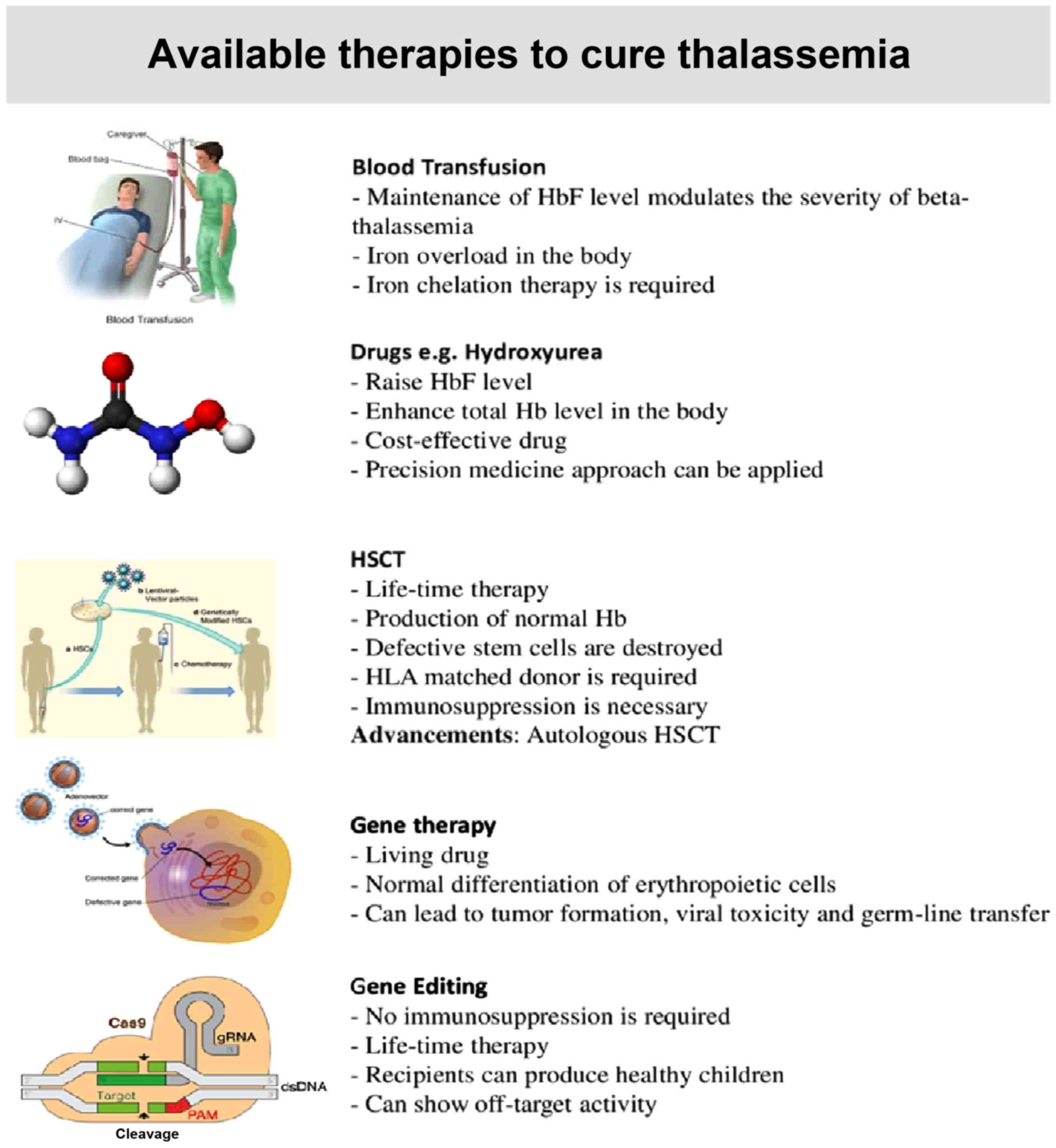 Novel Genetic Therapeutic Approaches For Modulating The Severity Of B Thalassemia Review
Novel Genetic Therapeutic Approaches For Modulating The Severity Of B Thalassemia Review

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.