Triggers of the disease have been elucidated and include factors such as trauma obesity infection stress and medications. Curr Probl Dermatol 2018531-14 13 Altenburg A Augustin M Zouboulis CC.
 Long Term Safety Of Biologics In The Treatment Of Psoriasis Ptt
Long Term Safety Of Biologics In The Treatment Of Psoriasis Ptt
Four of the six biologics we evaluated are FDA-approved to treat moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
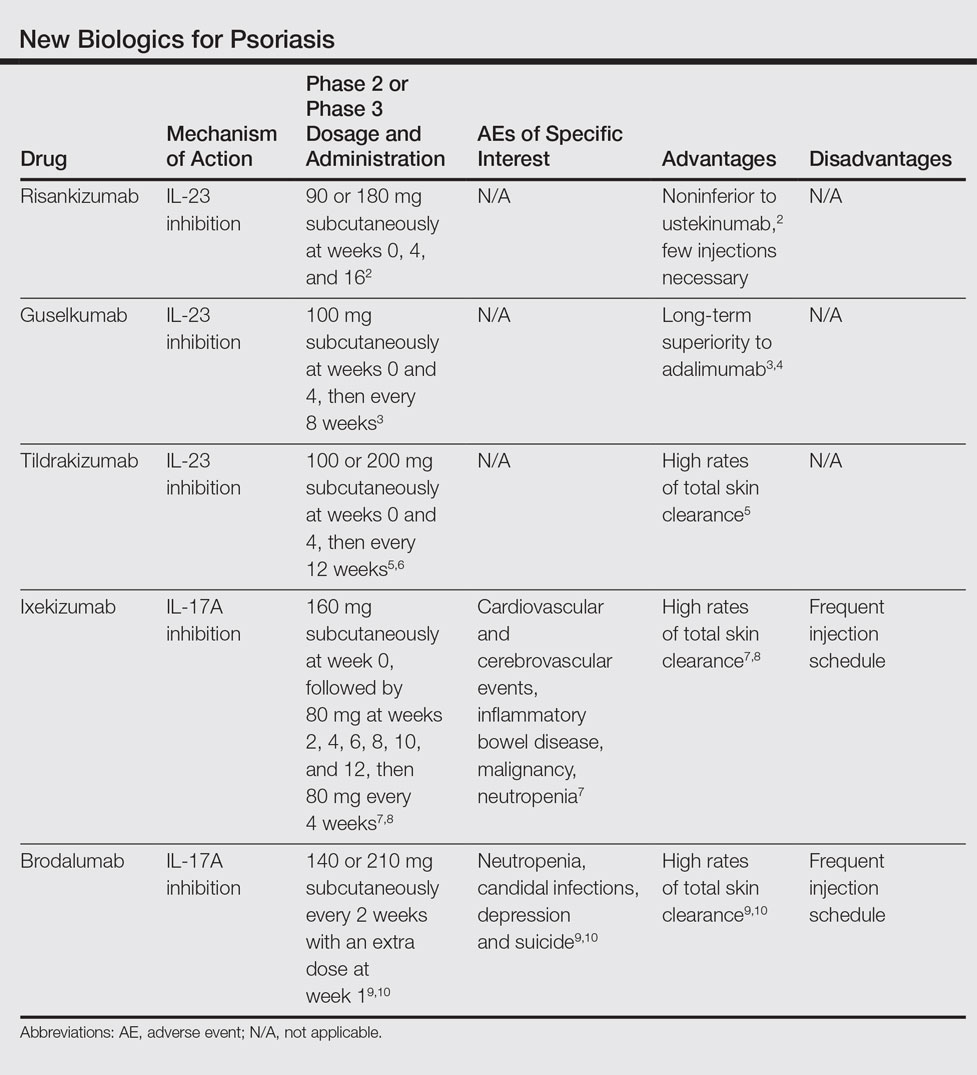
Biologics for psoriasis review. Relative to placebo and methotrexate all biologic agents had increased odds of efficacy at 10 to 16 weeks. Better understanding of those characteristic leads to the right choice for. Infliximab etanercept adalimumab certolizumab pegol interleukin IL-17 inhibitors secukinumab ixekizumab brodalumab an IL-1223 inhibitor ustekinumab and IL-23p19 inhibitors guselkumab tildrakizumab risankizumab 4 5.
12 Lockwood SJ Prens LM Kimball AB. Recent evidence supports the use of IL-17 antagonists. At its core psoriasis is a result of a dysfunctional immune response with T-cells at the center of immunogenesis.
Psoriasis is a multifaceted disease with a strong genetic component. Infliximab and ustekinumab have the most evidence of efficacy and safety for the treatment of pustular psoriasis. Our review shows that compared to placebo the biologics infliximab ixekizumab risankizumab bimekizumab secukinumab guselkumab and brodalumab were the most effective treatments for achieving PASI 90 in people with moderate-to-severe psoriasis on the basis of moderate- to high-certainty evidence.
In this paper we focus on the safety profile of biologics for psoriasis. The first biologic for psoriasis was approved in 2003. Biological therapy for pustular psoriasis.
Data from clinical trials and studies of the safety and efficacy of biologics provide essential information for the personalization of patient care. This NMA evidence is limited to induction therapy outcomes were measured from. However characteristics such as rapidity of onset long-term efficacy safety profile and effects on comorbidities are different.
Approved biologics for the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis include tumor necrosis factor inhibitors TNFi. Numerous pipeline biologic therapies including risankizumab guselkumab tildrakizumab. Alefacept is at present the only FDA-approved biologic for the treatment of psoriasis whereas efalizumab and etanercept are expected to gain.
Various biologic agents for psoriasis were effective at 12 weeks in placebo-controlled trials. Genetic data has revealed the presence of particular risk alleles in patients with psoriasis. Biologics currently approved for the treatment of psoriasis include tumor necrosis factor inhibitors interleukin IL-17 inhibitors ustekinumab an IL-1223 inhibitor and IL-23 inhibitors.
Biologics arent new. Available data cannot fully account for situations in clinical practice in which combination and longer duration of therapy may be required. In this article we review the literature on IL-23 and IL-17 inhibitors in the pipeline for use in moderate to severe psoriasis.
The purposes of this updated review of antipsoriatic biologic agents are to compare their pharmacologic properties and evaluate studies that address certain key clinical questions that are pertinent to the development of criteria for use of biologic agents for chronic plaque psoriasis CPP and psoriatic arthritis PsA in the Veterans. Over the last couple decades researchers have gathered quite a bit of evidence to support their safety and. Adverse reactions to biologics in psoriasis.
Adalimumab Humira etanercept Enbrel infliximab Remicade and ustekinumab Stelara. With the advent of biologics treatment of psoriasis dramatically changed due to its high efficacy and tolerable safety. A variety of biologic agents are available for the treatment of psoriasis nowadays.
A systematic review of biologics used in to treat palmoplantar psoriasis and palmoplantar pustulosis 2 diseases that affect the palms and the soles of feet found several available biologics are. As immune-related pathways involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis are elucidated new biologic treatments targeting these steps of the psoriatic immune cascade are developed. Comparative Efficacy of Biologics in Psoriasis.
The advent of biologics brought a paradigm shift in ways to treat psoriatic patients because they have dramatic efficacy. The biologics are the newest and most effective therapeutic weapon in the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis that can significantly alter the course of the disease in a relatively short period of time. As of 2017 six biologics are available in Japan.
The systematic literature review published in the Journal of Dermatological Treatment is one of the first pieces of evidence evaluating biologic therapy recommendations in psoriasis. At the same time safety concerns about biologics have been raised. Specifically biologic agents were associated with increased likelihood of achieving 90 improvement on Psoriasis Area and Severity Index or.
