A key component is tyrosine threonine kinase TTK also known as Mps1. The use of these drugs has also motivated pivotal advances in the understanding of the molecular biology of NSCLC including the discovery that mutations in EGFR are associated with dramatic and sustained responses to anti-EGFR treatments.
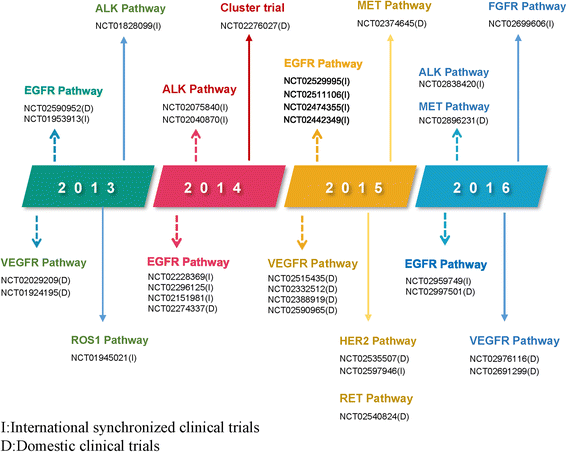 Clinical Trials Of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors For Lung Cancer In China A Review Journal Of Hematology Oncology Full Text
Clinical Trials Of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors For Lung Cancer In China A Review Journal Of Hematology Oncology Full Text
These significant advances have changed the clinical treatment of lung cancer in China and have led to a rapid development of clinical trials and consequently of new agents.

Tyrosine kinase inhibitors lung cancer. Epidermal growth factor receptor EGFR and its mutations are found to have an important role in this cancer. Targeted therapies especially Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor TKIs are widely used treatment option for this fatal disease with intriguing mechanism of action and many lessons being learned from them. Erlotinib was introduced as a second- and third-line therapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and demonstrated a survival advantage over placebo in unselected patients.
Einige Tyrosinkinase-Inhibitoren sind Medikamenten - Wirkstoffe die bisher vor allem bei Tumorerkrankungen zum Einsatz kommen. Mitsudomi Acquired resistance mechanisms to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer with activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutationdiversity ductility and destiny Cancer and Metastasis Reviews vol. Tyrosine Threonine Kinase Inhibition Eliminates Lung Cancers by Augmenting Apoptosis and Polyploidy The spindle assembly checkpoint maintains genomic integrity.
In recent years the management of lung cancer has been moving towards molecular-guided treatment and the best example of this new approach is the use of the tyrosine kinase inhibitors TKIs erlotinib and gefitinib in patients with mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor EGFR. Gefitinib which is a first generation TKI and Afatinib. The role of epidermal growth factor receptor EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors TKIs in the adjuvant treatment of non-small cell lung cancer NSCLC has not been well-established.
Moreover there has been a quick development of novel antineoplastic agents such as icotinib a first-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor TKI in China. Tyrosine kinases are largely deregulated in lung cancer and specifically in non-small cell lung cancer NSCLC. Tyrosinkinase-Inhibitor Tyrosinkinase-Inhibitoren sind Hemmstoffe die verschiedene Enzyme aus der Gruppe der Tyrosinkinasen hemmen.
Cancers that become resistant to Epidermal growth factor receptor EGFRspecific tyrosine kinase inhibitors through a secondary mutation are likely. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors TKIs against the human epidermal growth factor receptor EGFR are now standard treatment in the clinic for patients with advanced EGFRmutant non-small-cell lung cancer NSCLC. A real-world study in China Lung Cancer.
Publisher Site Google Scholar. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor TKI in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer NSCLC harboring uncommon EGFR mutations. Drugs that target the epidermal growth factor receptor EGFR have had a major impact on the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer NSCLC.
NSCLC constitutes about 85 of cases of lung cancer. Therefore EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors TKIs can work effectively against NSCLC. TTK antagonism is hypothesized to cause genomic instability and cell death.
Claiming the lives of the majority of patients afflicted by it. Bosutinib dasatinib EGF receptor saracatinib Src. Interestingly the clinical solidarity of these first generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors has become the prelude to a second wave of advances in molecular targeting that we can expect to further improve how we classify and treat lung cancers.
The tyrosine kinase inhibitors TKIs have revolutionized the treatment of lung cancer patients with respective mutations of so-called driver kinases and have demonstrated superior clinical activity compared to cytotoxic chemotherapy. It has two forms. Therefore the inhibition of pathogenic kinases is a breakthrough development in cancer research treatment and care which clinically improve the quality of life.
Cell lung cancer cell lines. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Could Be Effective Against Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Brain Metastases Harboring Uncommon EGFR Mutations Front Oncol. Lung cancer is one of the leading cause of cancer death globally.
We identified all patients with metastatic EGFR exon19del or L858R-mutant lung cancers treated with firstsecond-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors TKIs with pretreatment next-generation sequencing data MSK-IMPACT assay. Our meta-analysis aimed to determine whether the administration of EGFR-TKIs could improve the outcomes of patients with NSCLC undergoing complete resection. The effect of TMB on time-to-treatment discontinuation TTD and overall survival OS were evaluated in univariate and multivariate analyses.
This review summarizes the clinical development of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Small cell lung cancer SCLC and non-small-cell lung cancer NSCLC. MUC3A induces PD-L1 and reduces tyrosine kinase inhibitors effects in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer Int J Biol Sci.
First-generation EGFRTKIs binding competitively and reversibly to the ATP-binding site of the EGFRtyrosine kinase domain have resulted in a. Src tyrosine kinase inhibitors in clinical trials have shown a favorable safety profile and moderate anticancer activity in unselected patient populations. Future trials will continue to explore the contribution of Src inhibition in combination with chemotherapy and other targeted agents.
